Page 90 - วารสารปีที่16ฉบับที่2
P. 90
262
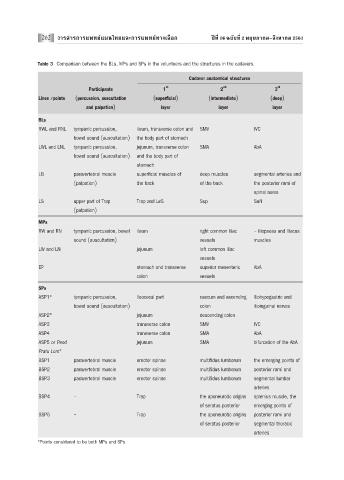
Table 3 Comparison between the BLs, MPs and SPs in the volunteers and the structures in the cadavers.
Cadaver anatomical structures
st nd rd
Participants 1 2 3
Lines /points (percussion, auscultation (superficial) (intermediate) (deep)
and palpation) layer layer layer
BLs
RWL and RNL tympanic percussion, ileum, transverse colon and SMV IVC
bowel sound (auscultation) the body part of stomach
LWL and LNL tympanic percussion, jejunum, transverse colon SMA AbA
bowel sound (auscultation) and the body part of
stomach
LB paravertebral muscle superficial muscles of deep muscles segmental arteries and
(palpation) the back of the back the posterior rami of
spinal nerve
LS upper part of Trap Trap and LeS Sup SuN
(palpation)
MPs
RW and RN tympanic percussion, bowel ileum right common iliac - iliopsoas and iliacus
sound (auscultation) vessels muscles
LW and LN jejunum left common iliac
vessels
EP stomach and transverse superior mesenteric AbA
colon vessels
SPs
ASP1* tympanic percussion, ileocecal part caecum and ascending iliohypogastric and
bowel sound (auscultation) colon ilioinguinal nerves
ASP2* jejunum descending colon
ASP3 transverse colon SMV IVC
ASP4 transverse colon SMA AbA
ASP5 or Peod jejunum SMA bifurcation of the AbA
Pratu Lom*
BSP1 paravertebral muscle erector spinae multifidus lumborum the emerging points of
BSP2 paravertebral muscle erector spinae multifidus lumborum posterior rami and
BSP3 paravertebral muscle erector spinae multifidus lumborum segmental lumbar
arteries
BSP4 - Trap the aponeurotic origins splenius muscle, the
of seratus posterior emerging points of
BSP5 - Trap the aponeurotic origins posterior rami and
of seratus posterior segmental thoracic
arteries
*Points considered to be both MPs and SPs